What is an Overhung Load Adaptor (OHLA)?
An Overhung Load Adaptor is a compact bearing housing with an integrated bearings and output shaft that is mounted between a drive (e.g. hydraulic motor, electric motor or gearbox) and a mechanical load.
The goal is to transfer overhanging radial and axial forces from the drive shaft to the OHLA in order to protect the drive. These forces are generated, for example, by mounted pulleys, gear wheels, sprockets or translational loads (e.g. screw conveyors or linear drives), which would act directly on the drive shaft.
🔧 Main functions of an Overhung Load Adaptor:
- Absorption of radial and axial forces (e.g. from pulleys, sprockets, chain wheels, couplings).
- Protection of the drive (e.g. hydraulic motor, electric motor or gearbox) from excessive loads.
- Shifting the load point from the motor bearing to the robust OHLA bearing.
- Torque transmission remains guaranteed.
- Integrated contamination barrier provides protection against contamination
- Face and foot mounting option
- and much more.
🛠️ Typical design:
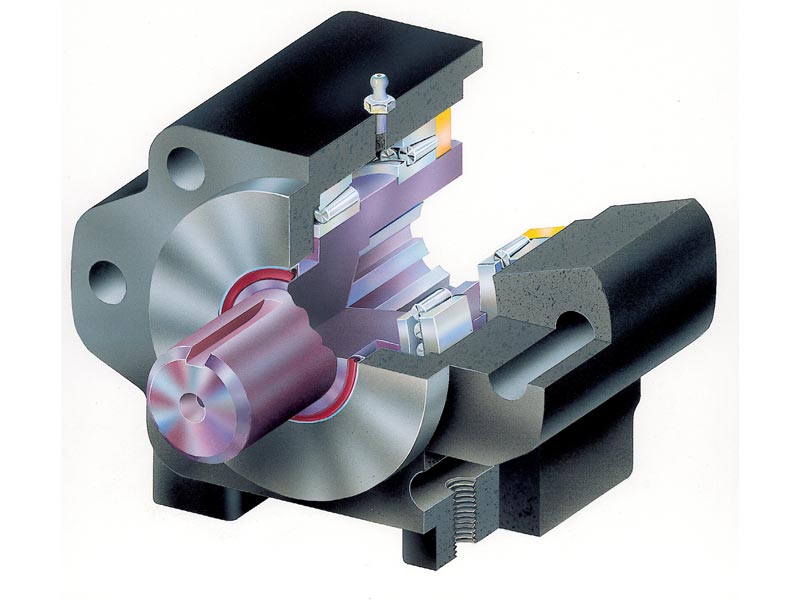
- Housing:
- Robust cast housing
- Precisely machined mounting surfaces and bores for axial and radial alignment with the drive unit
- Integrated mounting threads or flange surfaces for mounting on the motor or machine
- Shaft bearing arrangement:
- Heavy duty bearings:
- Heavy-Duty spherical roller bearings (for combined radial & axial forces)
- or Deep-grooved ball bearings
- The bearings are mounted in precise fits in the housing, with defined preloads for backlash-free operation and durability
- Shaft (Output):
- Connection of the OHLA to the drive system (e.g. coupling, chain, gear wheel)
- Mounting e.g. with feather key, splined shaft or multi-tooth profile
- Sealing system against contamination and leakage (contamination barrier)
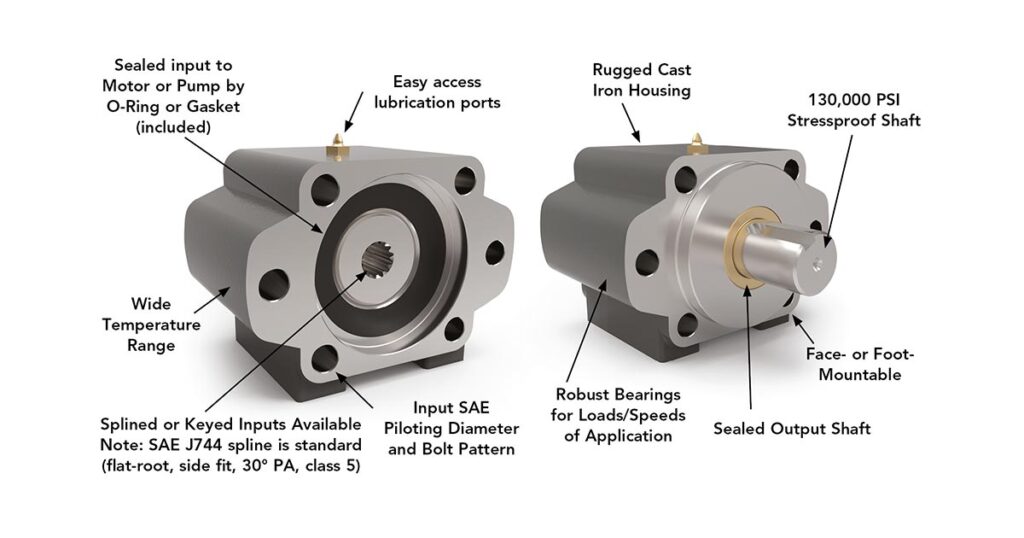
- Mounting flange:
- Suitable for standardized hydraulic motors (e.g. SAE A-F)
- Alternative: standard flanges (NEMA, ISO, IEC, ISO)
- Customer-specific connections with centering and mounting holes
- Sealing system
- Radial shaft seals or labyrinth seals protect bearings and interiors against dust, dirt, moisture or escaping lubricants
- Depending on the environment, also designed as a multiple sealing system (e.g. for construction or off-road machines)
- Lubrication
- Bearings are greased at the factory (maintenance-free) or can be regularly maintained via grease nipples
- High-temperature grease or special lubricants for industrial and heavy-duty applications
📦 Examples of applications:
🚜 1. Agricultural and construction machinery
- Excavator hydraulic motors with side drive: e.g. chain drive via gear wheel or chain
- Harvesting machines: e.g. drive of screw conveyors, chain drives or power take-off shafts (PTO)
- Forestry machines: e.g. on pulley and toothed belt systems on cutting rotors on forestry shredders or mulchers
- Wheel loaders or tracked vehicles: Protection of the wheel hub drives when loads are applied from the side
🏗️ 2. Conveyor technology & material handling
- Belt conveyors: drive pulleys with high belt tension
- Roller drives: for heavy goods or high lateral forces
- Sorting systems: e.g. for pallets or parcels
🛠️ 3. Mechanical and plant engineering
- Screw conveyor: Motor mounted at the front, screw generates axial load
- Hoists / cable winches: Cable pulleys exert axial forces on the drive shaft
- Industrial agitators: Transverse loads due to liquids and shaft vibration
🛢️ 4. Oil & Gas industry / offshore
- Pump drives with pulleys: e.g. for drilling rigs or frac units
- Pipe extraction machines: with highly eccentric load support
🚀 5. Special machines & test benches
- Test benches with shifting torques: e.g. for electric motors or couplings
Test systems for belt drives: controlled application of force to the test object
⚓6. Maritime applications
- Deck winches & cable winch drives: Drive winches for anchors, mooring lines or towing lines
- Hydraulic and centrifugal pumps on board: ballast water pumps, cooling water, fire extinguishing systems
- Shaft drives: Mechanically driven propeller or thrust systems

✅ Reasons for using overhung load adaptors – with examples
- High radial and axial loads on
the output shaft
→ e.g. for belt or chain drives that pull strongly sideways
→ Example: Conveyor belt drive in a rock crushing system - Protection of pumps, gearboxes
or motor bearings against overload
→ OHLA absorbs the bearing forces, not the connected device
→ Example: Hydraulic pump on a wheel loader - Extending the service life of
sensitive components
→ Significantly reduces bearing and shaft wear or damages
→ Examplel: Electric motor in a mobile forestry machine - Shaft misalignment or
misalignment in the structure
→ OHLA can absorb slight misalignments
→ Example: Installation in compact tunnel boring machine with limited installation space - Use in harsh environments with
high levels of dust or dirt
→ OHLA with reinforced seal protects the inner components
→ Example: Use on a mobile rock drill in opencast mining - Easier servicing due to
decoupled assemblies
→ Components can be replaced faster
→ Example: Replacement of a hydraulic motor in the quarry conveyor truck
🧰 In summary, wherever:
- the drive unit cannot or should not absorb all the forces/loads itself
- lateral (radial) loads occur, e.g. due to belts, chains, gear wheels
- high axial loads caused by pressure or tension
Need technical details or special solutions? Our team will be happy to assist you.
